Demystifying Networks: How it Work and Why Matter

Networks are the silent heroes of our digital world, powering everything from the local printer in your office to the vast expanse of the internet. But have you ever stopped to wonder how they actually work? Let’s dive into the fascinating world of network communication and unlock its secrets.
The Building Blocks:
Devices: The stars of the show! Computers, printers, phones, servers – they all become part of the network, ready to share information.

Networking Devices: The traffic cops directing the flow. Routers, switches, and firewalls ensure data reaches the right destination and stays safe
Routers: Routers connect different networks, directing data traffic between them. They play a crucial role in determining the most efficient path for data to travel.
Switches: Switches operate within a single network, forwarding data only to the device it is intended for. They enhance the efficiency of data transmission within LANs.
Firewalls: Firewalls protect networks by monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic. They act as a barrier against unauthorized access and potential cyber threats.
Protocol
The unspoken language of the network. Rules and formats dictate how devices communicate, like TCP/IP for the internet.

TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol): The foundation of the internet, TCP/IP ensures reliable and orderly data transmission between devices.
HTTP/HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol/Secure): Used for web communication, HTTP and HTTPS enable the transfer of information between web browsers and servers.
DNS (Domain Name System): DNS translates human-readable domain names into IP addresses, allowing us to access websites using names like www.example.com instead of numerical IP addresses.
The Flow of Information:
- Initiation: You click a link, send an email, or print a document. Your device initiates the process.
- Packaging: The information gets chopped into bite-sized packets, each with a header like an address label.
- Transmission: Packets ride through the network connections, hopping between routers and switches like digital hitchhikers.
- Delivery: Packets reach their destination device, the address guiding them like a treasure map.
- Reconstruction: Packets reunite, reassembled into the original information – your email arrives, the document prints.
Benefits of Networking:
- Resource Sharing: Printers, files, even internet access can be shared, maximizing resources and saving costs.
- Collaboration: Teams can work together on projects in real-time, regardless of location, boosting productivity.
- Communication: Emails, instant messaging, video conferencing – networks keep us connected with anyone, anywhere.
- Information Access: A world of knowledge at your fingertips with online databases, libraries, and educational resources.
Beyond the Basics:
- Network Security: Firewalls and encryption safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Network Troubleshooting: When things go wrong, understanding basic network principles helps diagnose and fix issues.
- Network Types: From small home networks to massive global networks, each serves a specific purpose.
Types of Networks:
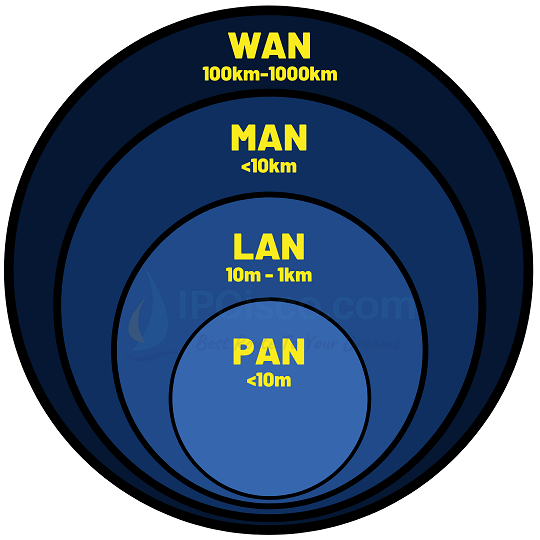
Local Area Networks (LANs): LANs are confined to a specific geographic area, such as a home, office, or campus. They facilitate high-speed communication among devices in close proximity.
Wide Area Networks (WANs): WANs cover a broader geographical area and connect LANs over long distances. The internet itself is a vast global WAN that interconnects countless networks worldwide.
Wireless Networks: Wireless networks use radio waves or infrared signals to transmit data without physical cables. Wi-Fi is a common example found in homes, cafes, and public spaces.
Cloud Networks: Cloud computing relies on networks to provide scalable and flexible resources over the internet. Cloud networks enable on-demand access to services and data storage.
The Future of Networking:
As technology advances, so does the landscape of networking. Concepts like 5G, the Internet of Things (IoT), and edge computing are reshaping how we connect and communicate. These developments promise faster, more reliable, and secure networks for the future.
Conclusion
In essence, networks form the digital arteries of our interconnected world, enabling seamless communication and access to information. Understanding the fundamentals, types, protocols, devices, and security aspects of networks empowers individuals and organizations to navigate this complex web of connectivity with confidence. As we continue to push the boundaries of technology, the evolution of networks will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of our interconnected society.




